- Department:Chemicals Administration Ministry of Environment
Since the launch of the Toxic and Chemical Substances Bureau (TCSB) of the EPA in the end of 2016, the EPA focused on gradually strengthening the management of chemicals which are harmful to human health and the environment. Operation, controls, and flow tracking on toxic chemicals, chemical raw materials, and food additives are also strengthened. The EPA inspected over 3,000 chemical raw material enterprises in both 2017 and 2018, and declared 27 chemicals, including Sudan Red, as toxic chemical substances that are illegal to be used in food. Moreover, the EPA will continue close collaborations on tightened chemical substance management with the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) to prevent non-food grade chemicals from entering the food product chain systematically to safeguard food safety and citizens’ health.
The EPA has experienced several occasions on which toxic chemicals were found in food products in the past, such as the Rhodamine B found in glutinous rice calls, metanil yellow and dimethyl yellow in dried tofu, maleic anhydride in starch, Sudan Red G in salted duck yolks for mooncakes, etc. Therefore, to prevent toxic chemical substances from contaminating, the EPA has divided the control measures in two categories: policy making and source control.
To regulate by laws and control at source, the EPA banned the use of 13 harmful chemical substances (e.g., Rhodamine B) in food on 26 September 2017. Companies that use these 13 substances in their products are stipulated to submit their operation reports regularly, clearly label all containers/packaging and handling premises, prepare material safety data sheets (MSDS), and obtain approval documents.
Moreover, the EPA declared on 28 June 2018 another 14 chemicals, including Sudan Red, as toxic chemical substances that are illegal to be used in food.
Companies that manufacture products containing these 14 substances shall start reporting operations from 1 January 2019. Additionally, all containers/ packaging and handling premises have to be labeled and material safety sheets completed by 1 July 2019. Companies must also acquire approval documents by 1 January 2020, which will be reviewed. To ensure the management and tracking of the chemical substances, approval documents are not to be used by other parties.
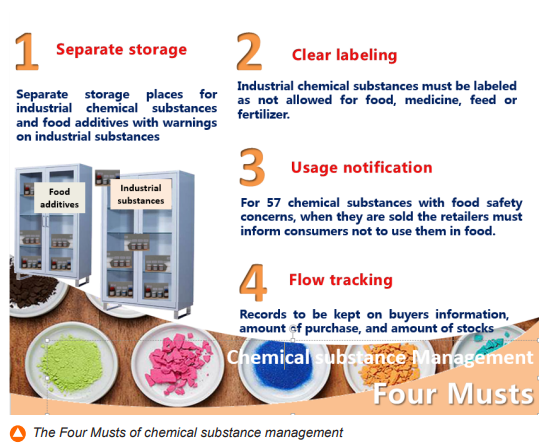
To enhance the source control, the EPA inspected over 3,000 chemical raw material enterprises in both 2017 and 2018. During the inspection visits, the EPA also informed the companies of the “four musts” of chemical substance management for food safety, which include: separate storage, clear labeling, usage notification, and flow tracking. The EPA will continue to investigate more companies in 2019. Also, the EPA has been working with health and agricultural agencies to conduct joint inspections around special holidays and did not find any banned toxic chemicals in food products in 2018.
The EPA stressed that food safety managment is a collaboration between and carried out by the central and regional governments. They are in charge of inspecting enterprises’ management of toxic chemicals, providing assistance on voluntary chemical management, food enterprise registration, random inspections for labels of food additive products, and food additive management. Besides re-inspections of chemical raw material suppliers in 2018, the 2018 Egg Farmers’ Chemical Substances Self-Management Improving Plan was also implemented. Instruction on four principles for farm chemical substance controls were given as well, namely: clarifying origins, applying chemicals correctly, using chemicals safely, and storage management.
The EPA emphasized its determination to continue close collaborations with MOHW on tightened chemical substance management. Operation, controls, and flow tracking of toxic chemicals, chemical raw materials, and food additives are also strengthened. If discovered, all illegal operations and additions will be punished in accordance with the Toxic and Concerned Chemical Substances Control Act ( 毒性及關注化學 物質管理法 ) and the Act Governing Food Safety and Sanitation ( 食品安全衛生管理法 ).
Source: EPA Major Environmental Policies, March 2019